In today’s digital age, finding clear guidance on how to start a bank can be like searching for a needle in a haystack.
The available information often lacks organization and may even provide conflicting advice.
Relatable? Well then, you’ve come to the right place.
Even in the age of online banking, starting a bank remains complex and highly regulated.
That said, things get a lot easier once you know the procedure. Afterward, it’s all about defining your business and getting the right documents together.
In this article, you’ll learn the step-by-step process of how to start a bank. We’ll cover every important aspect, beginning with market research and extending to topics like mandatory permits and insurance coverage.
Without further ado, let’s get started.
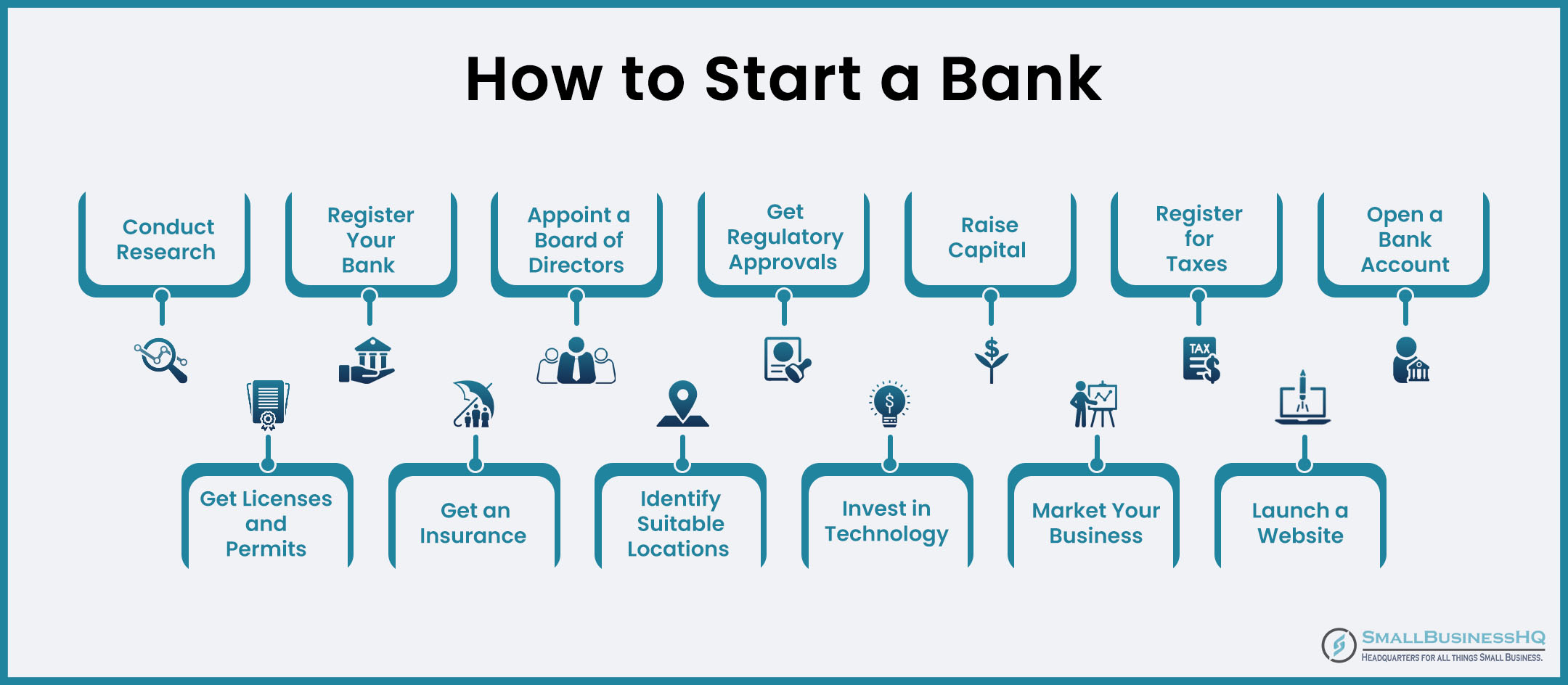
Step 1: Do Some Research and Planning
Setting the groundwork should be the first step in starting any venture, and starting a bank is no exception. This will keep you from going off track as you learn how to start a bank.
Conducting thorough market research will give you insights into:
- The broader market dynamics
- Cost considerations
- Achieving profitability
- Demographics of your target market
- Your business plan
Now, let’s look at each of these factors in more detail.
Study the Market Landscape
Examining the banking landscape within your intended geographic area is a good place to start.
You can start by defining your target customer base. Then, start evaluating the demand for banking services in your target area. Oftentimes, bank startup entrepreneurs identify gaps within the market that their own bank could address.
Finally, survey existing banks and financial institutions operating in your chosen market. Check out their product portfolios, pricing strategies, customer service quality, and market positioning.
You can also use Porter’s Five Forces model to study the industry competition. It will help you understand the following market forces:
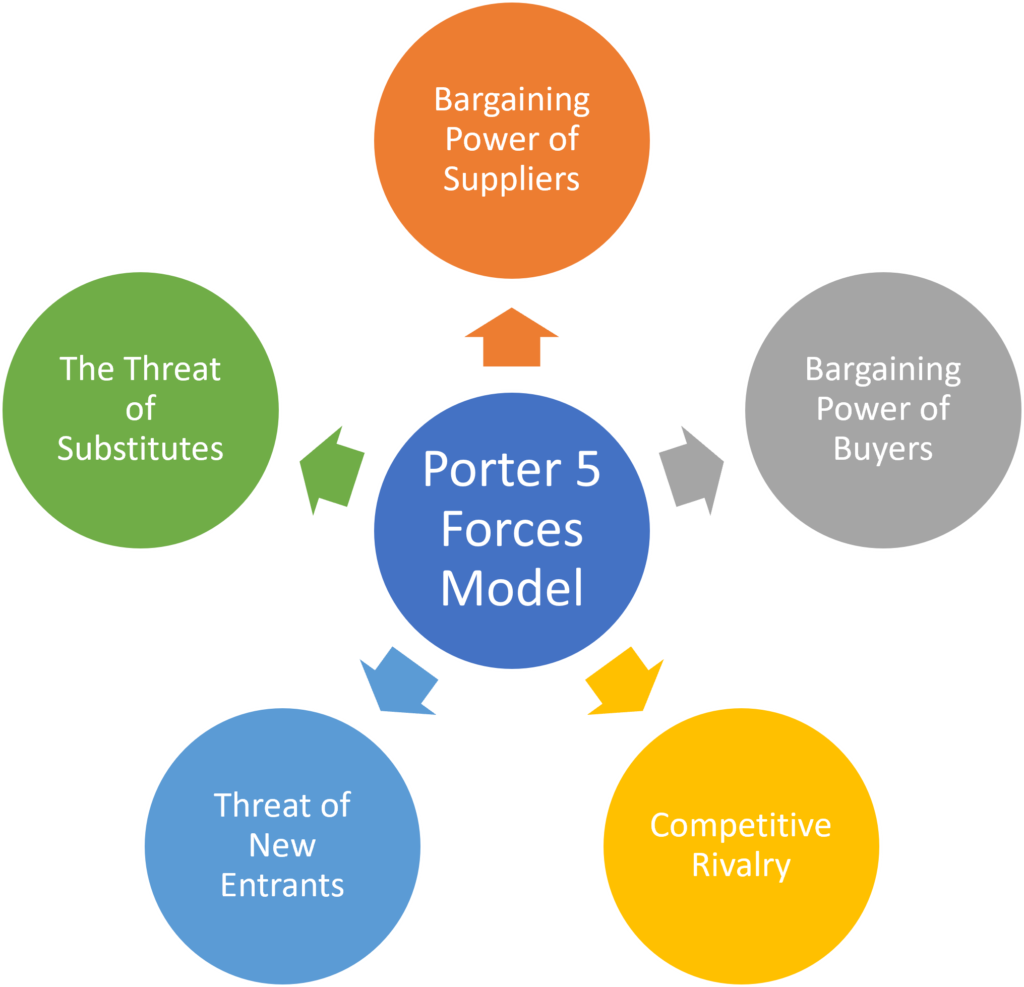
Image via SimpliMBA
Understand the Costs Associated with Starting a Bank
Starting a bank in the United States involves a range of expenses. These costs vary based on factors like the bank’s size and location.
Here’s a list of some of the key costs you should know of before you start a bank:
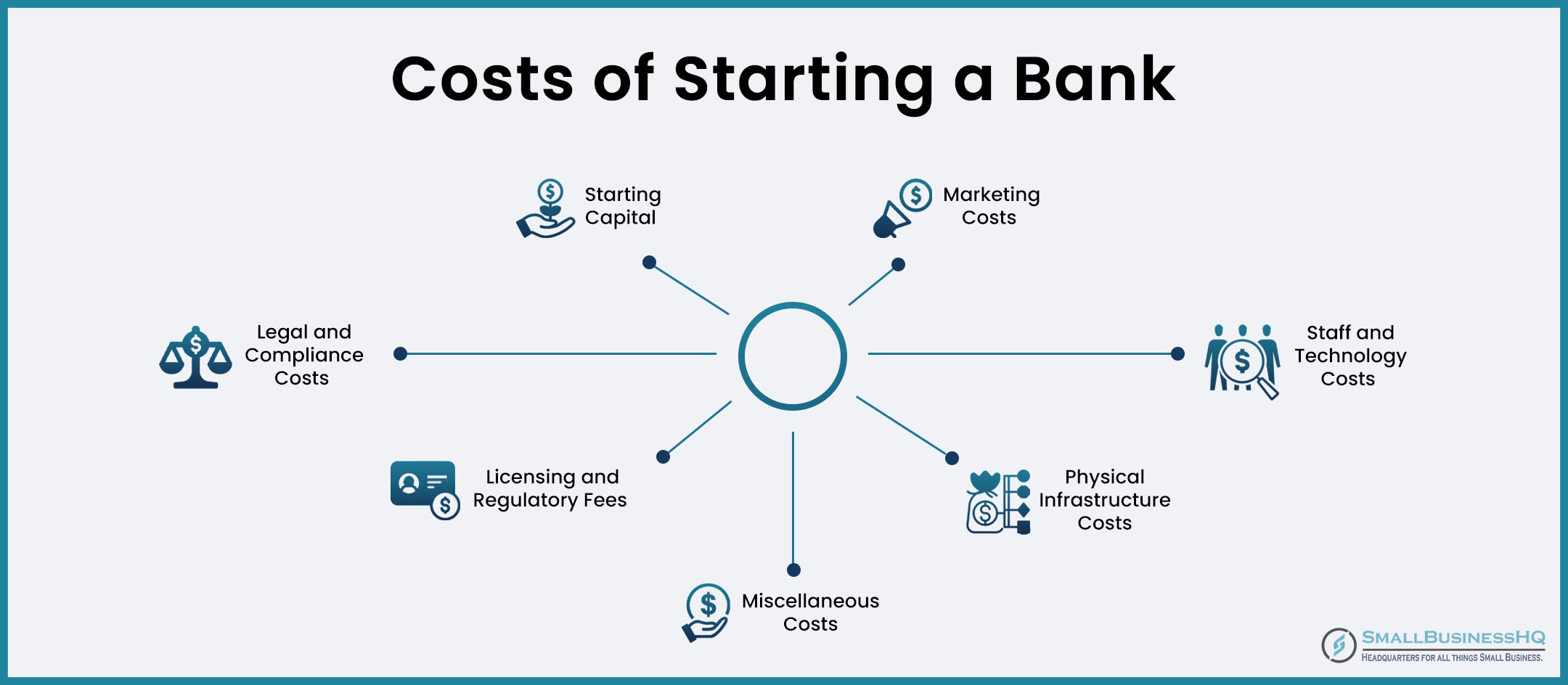
- Starting capital: To start a bank, you must have an initial capital ranging from $12 million to $20 million.
- Licensing and regulatory fees: This covers costs of obtaining the necessary licenses and permits. It includes fees for federal and state banking regulators.
- Legal and compliance costs: You’ll have to shell out money for things like drafting contracts and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Physical infrastructure costs: Cost of renting or purchasing an office space for your bank, including the cost of furnishings and equipment.
- Staff and technology costs: These are recurring expenses you’ll incur to start a bank and keep it running.
- Marketing and promotion costs: Building a customer base requires marketing, which will be an ongoing expense.
- Other costs: Additionally, there will be other costs such as insurance, accounting services, advisory fees, etc.
Make a Plan for How Your Bank Will Make Money
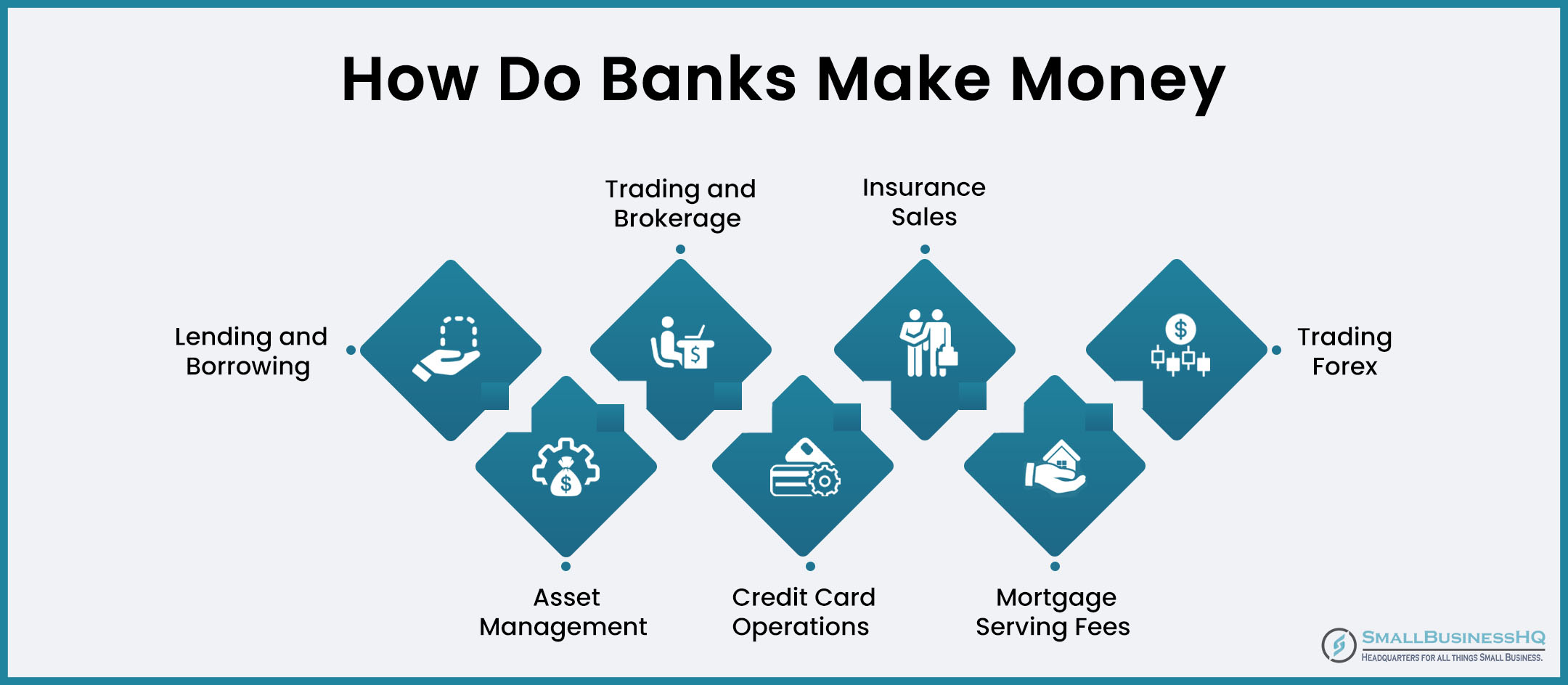
Banks make money by accepting deposits from individuals and businesses and then lending those funds to borrowers.
Imagine a bank that collects deposits at a 0.07% interest rate from the public. It then lends this money to borrowers at higher market rates. The profit, referred to as the “interest spread,” is the difference between both rates.
However, this is just the tip of the iceberg. Banks generate income from various other sources, some of which are listed below:
- Asset management
- Trading and brokerage
- Credit card operations
- Insurance sales
- Mortgage servicing fees
To make your bank more profitable, it’s essential to offer more than just basic services like savings accounts.
Develop a Business Plan
A comprehensive business plan is like the blueprint for your bank’s success. It spells out your bank’s vision, mission, and goals in plain language.
Additionally, it should lay down the types of financial products and services you intend to offer. Equally important is establishing effective pricing models to balance competitiveness and profitability.
Lastly, create a financial plan, and include outlines, goals, and estimates. This will not only attract investors but also provide a roadmap for financial stability and future growth.
The expert business advisors at companies like Inc Authority and ZenBusiness can help you chalk out a strong business plan, setting you up for success.
Step 2: Register Your Bank
The foundation of every startup bank begins with the establishment of a legal entity. This provides protection for personal assets and liabilities while also offering opportunities for tax advantages.
Let’s discuss the step-by-step process to start a new bank.
Choose a Legal Structure
When learning how to start a bank, one of the first crucial steps is selecting the right legal business structure. Two primary options stand out: Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) and Corporations.
Which one should you pick?
Well, the choice depends on factors like bank size, ownership structure, governance preferences, and tax considerations.
LLCs provide more flexibility with fewer regulatory demands, limited liability, and pass-through taxation. Conversely, Corporations offer a more formal structure with greater regulatory oversight but potential double taxation.

You May Also Like:
Register the Entity
Next, register the chosen legal structure with the appropriate government authorities. This involves filing articles of incorporation or organization with the state or country where your bank will be based.
Again, you use the services of business formation service providers to register your new business with the state.
Step 3: Appoint a Board of Directors
If you choose to form a Corporation, you’ll need to appoint directors.
Form a board of directors that will oversee the management of the bank. Try to aim for a diverse group with experience in business, banking, and other relevant fields.
This is something that’s taken seriously by government regulators and investors when assessing the institution.
Step 4: Get Regulatory Approvals
Send an application to the appropriate banking regulatory body to get the approval to start your banking operations.
This involves giving a detailed account of your bank’s business plan, capital setup, risk management infrastructure, management team, and how well you adhere to regulations.
Expect a rigorous regulatory process, including background checks on your team and an examination of your bank’s financial health.
For a smooth process, consider working with firms like IncFile and LegalZoom.
Step 5: Raise Capital
Once you obtain approval, you must secure initial capital to start operations. Some potential sources of capital are private investors, community investments, government grants, bank loans, and online crowdfunding.
Even after you start your bank, it’s essential to regularly assess your finances and conduct stress tests. These checks ensure you have enough capital to meet regulatory requirements and maintain financial stability.
Step 6: Register for Taxes
When you start a bank, you need to register for a range of state and federal taxes.
This will entail completing the requisite tax forms, obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, and registering with your state’s revenue agency.
Additionally, it’s essential to stay informed about tax compliance obligations, including deadlines for filing and payment.
Companies like IncAuthority and LegalZoom provide tax planning consultations to help you maximize your tax advantages.
Step 7: Open a Bank Account
A bank requires a bank account as well.
By taking this step, you protect your personal assets, such as savings, investments, and property, from potential legal claims or lawsuits that your business might encounter.
This account will also facilitate various financial activities, including depositing customer funds, disbursing loans, processing payments, and conducting regulatory reporting.
Depending on your specific banking needs, it may also make sense to get a business credit card. Credit cards provide bank owners with a source of short-term financing, while also building their bank’s credit history.
There are several companies that simplify the process of creating a business bank account—Incfile, ZenBusiness, and LegalZoom, to name a few.
Step 8: Obtain Necessary Licenses and Permits
Without a banking license, attempting to start a bank or performing banking activities is illegal in most jurisdictions.
Furthermore, these licenses and permits often include consumer protection measures, fostering trust in the financial community.
So, which licenses do you need to start a bank?
Well, banks typically need licenses at various levels, including federal, state, and local. The specific requirements can vary significantly by location.
Here are some licenses you may need when starting a bank:
- Certificate of Occupancy (CO): If you are setting up physical branches or offices, you may need a CO for those locations.
- Business licenses and permits: These can include local business licenses, zoning permits, and other municipal authorizations.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance: You may need to obtain permits or licenses to ensure you can verify the identities of your customers and report suspicious transactions.
In the same vein, if the proposed bank wants to branch out into services like insurance, money transfers, or investments, it’ll require extra licenses.
Companies like Incfile and Inc Authority can help you quickly obtain the necessary licenses to start a bank.
Step 9: Secure Insurance Coverage
When considering how to start a bank, it’s crucial to understand the requirements for insurance. In many jurisdictions, some types of insurance like liability coverage are legally necessary.
Apart from that, here are some common types of insurance that banks may need:
- General Liability Insurance: This offers crucial protection against liabilities that can arise in day-to-day operations.
- Deposit Insurance: Mandatory for most banks, this insurance protects depositors in case of bank failure.
- Cybersecurity Insurance: This insurance helps banks recover from cyberattacks, data breaches, and other technology-related risks.
- Workers’ Compensation: It provides coverage for employees who are injured or get ill while performing their official duties.
Before you start a bank, take some time to identify potential risks and liabilities. This will help you figure out what kinds of insurance you need. You can even seek advice from experts at companies like IncAuthority and ZenBusiness to get more clarity.
Step 10: Identify Suitable Locations
Now, let’s dive deeper into how to start a bank with a focus on non-regulatory aspects.
Many Americans are shifting to online banking, leading to a decline in foot traffic at traditional brick-and-mortar banks. This isn’t to say that you should skip having a physical location, but it’s important to be mindful of this trend.
A good location for newly established banks is one that’s easy for your customers to access. Don’t forget that some states have specific rules about where banks can set up shop.
Moreover, think about the costs. Figure out if you can afford to lease or buy in a particular area.
Step 11: Invest in Technology and Staff
With the rising popularity of online banking services, it’s crucial to invest in top-notch technology.
Here are things you should invest in when you start a bank:
- Mobile app: Develop a user-friendly application to cater to customers’ mobile banking needs. Ensure it offers features like balance checking, fund transfers, and mobile check deposits.
- Cloud computing: This allows easy expansion of services and storage capabilities as your bank grows.
- AI chatbots: Use AI-powered chatbots to offer instant responses to customer inquiries and enhance customer service efficiency.
- Automated Teller Machines (ATMs): Install ATMs at strategic locations, providing convenient access to cash for bank customers and non-customers alike.
- Cybersecurity solutions: Invest in robust cybersecurity tools to safeguard customer data and protect your bank against cyber threats. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption technologies.
Simultaneously, your staff plays a pivotal role as the face of your bank. Training them for exceptional customer service and regulatory compliance is paramount.
They’re your first line of defense in keeping customer data secure, making staff cybersecurity awareness crucial.
Step 12: Market Your Business
Once you’ve settled on the ideal location, assembled your tech infrastructure, and trained your staff, it’s time to get the word out to potential customers.
First things first, develop a distinctive brand identity for your bank. This includes creating a memorable logo, crafting a unique value proposition, and defining your bank’s mission and vision.
As for marketing strategies, here are some effective ones to consider:
- Social media marketing: Small banks can share financial tips, news, and updates on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
- Content marketing: Create a variety of content that solves users’ problems and covers trending topics. Start a blog, create videos, or use social media to share content that resonates with your audience.
- Email marketing: As a small bank, you should invest in email marketing as it’s a cost-effective technique. You can send emails about new services, share money-saving tips, or give updates on accounts.
- Traditional advertising: Older consumers typically prefer traditional media like newspapers and TV. Some of your options for traditional marketing are print ads, radio commercials, and billboards.
Here’s an example showing how Bank of America uses social media to share its values and company culture.
Image via LinkedIn
Step 13: Set up a Website and Phone System
Creating a website and setting up your phone system is like giving your bank a virtual storefront and a friendly voice.
For your website, get a domain name that matches your brand name and invest in a solid hosting service.
Design a professional website that reflects your bank’s brand identity, making sure it’s responsive for mobile users. Then, fill it with information about what you offer, where you are located, and how people can reach you.
Companies like IncFile and ZenBusiness offer more services than just business formation; they also assist with website creation. Check these out to get help with website creation and domain registration.
As such, some people still prefer traditional communication methods like phone calls. This may be because phone communication:
- Allows for a more personalized customer experience
- Makes detailed discussions and problem-solving possible
- Helps customers get immediate assistance
- Assures customers that there is a real team behind the operations
That’s why you should set up lines for all sorts of customer needs — questions, support, general information, etc. It is highly recommended for banks to use an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system to direct calls efficiently.
Also, be clear about when you’re open for business and how to reach you in case of banking emergencies.
FAQs
Q1. How much does it cost to start a bank?
A. The cost of starting a bank can vary significantly depending on various factors.
In the United States, the initial capital requirement is typically in the range of $12 million to $20 million or more. This capital is needed to meet regulatory requirements and ensure the bank’s financial stability.
Recurring costs involve technology and infrastructure expenses, leasing or purchasing physical premises, staffing, marketing, and ongoing operations.
Q2. Can anyone just start a bank?
A. No, starting a bank is not open to just anyone. It involves navigating a highly complex regulatory process.
This includes obtaining regulatory approval, meeting capital adequacy requirements, assembling a qualified team, and establishing operational infrastructure.
The process demands substantial financial resources and lending expertise.
Q3. Can an individual own a bank?
A. Yes, an individual can own a bank. However, in most countries, this is highly unlikely due to the significant regulatory and minimum capital requirements.
Banks also require the presence of experienced bankers and a robust infrastructure. As a result, ownership and governance of banks typically have to do with financial institutions or investor collectives.
Q4. How much does owning a bank make you?
A. The potential earnings from owning a bank vary depending on various factors. Most banks usually see about 10-15% in profit, with a return of 7-10% on their investments.
For online banks, the potential for substantial profits exists, especially if the bank offers a diverse range of services, a broad customer base, and effective risk management strategies.
In contrast, smaller community banks may have lower profit potential, but their owners benefit from closer ties to the local community and a more personal banking experience.
Q5. How can I start a bank without money?
A. If you’re wondering how to start a bank with no money, it’s essential to understand that this is highly improbable. The bank would not meet the regulatory requirements necessary for its operation and lack financial resources.
It’s essential to work closely with financial experts to navigate the process of starting a bank.
Final Thoughts: How to Start a Bank?
In a nutshell, figuring out how to start a bank is a huge task that needs a lot of commitment, financial planning, and following the rules.
Whether you’re considering starting a traditional bank or a modern digital one, the journey is complex. It involves gathering funds, creating a solid plan, building a top-notch team, and navigating the maze of regulations.
Yet, for those with a strong vision and determination, the banking industry can be rewarding.
Starting a bank is more than just a business; it’s a way to help communities, fuel economic growth, and be part of the ever-changing world of finance.
















